Behavioral Modeling
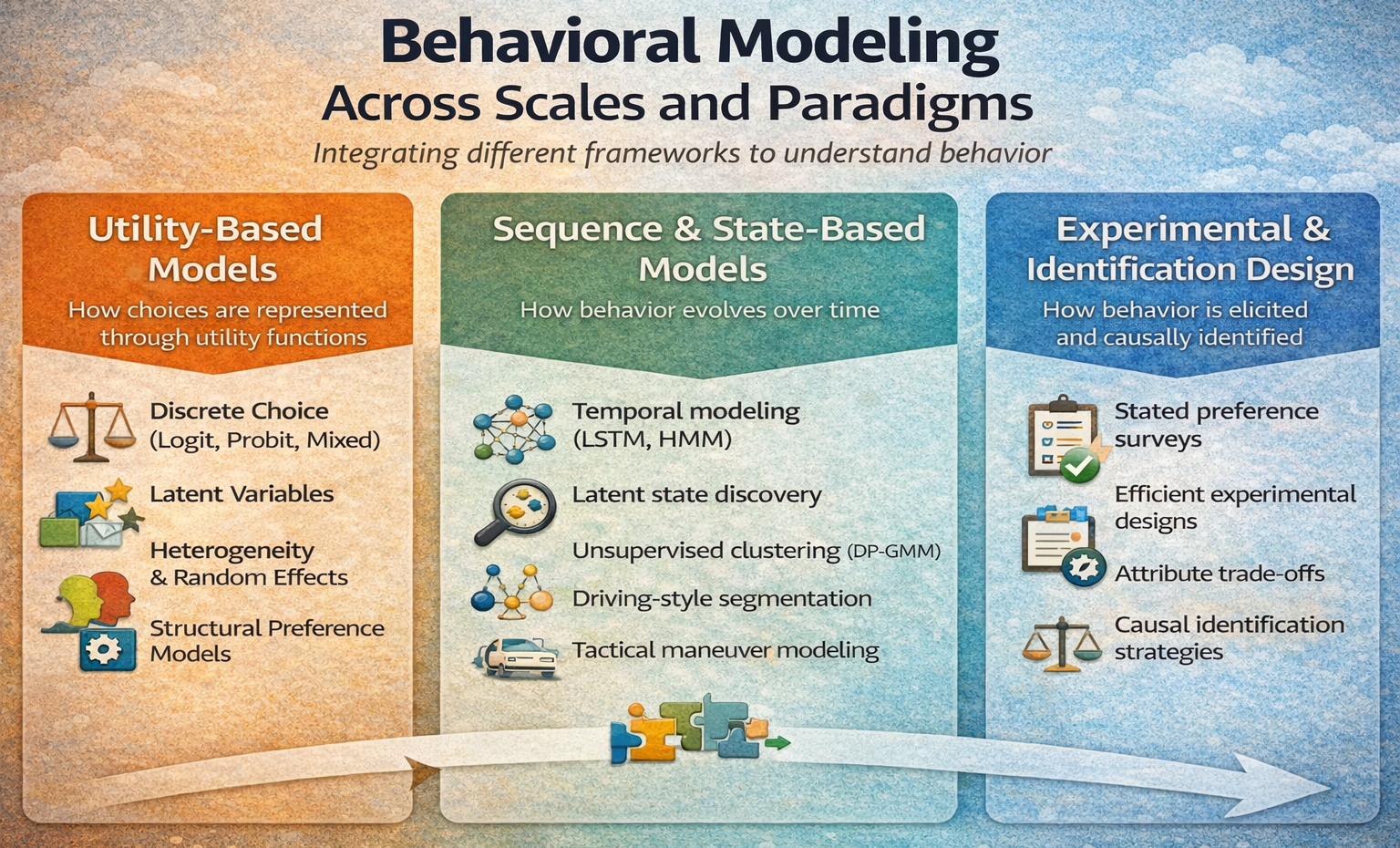
Behavioral modeling and analysis focus on understanding, quantifying, and predicting how individuals and groups make decisions under constraints, uncertainty, and trade-offs. At its core, it treats behavior as an observable outcome of latent preferences, perceptions, incentives, and contextual factors, translated into measurable choices and actions. This perspective is widely applicable across domains, ranging from mobility and energy use to marketing, finance, and human–AI interaction, because it combines rigorous statistical modeling with data-driven inference to explain why decisions are made, not only what happens. For data science practice, behavioral analysis provides a structured way to link raw data to interpretable insights, policy levers, and operational decisions.
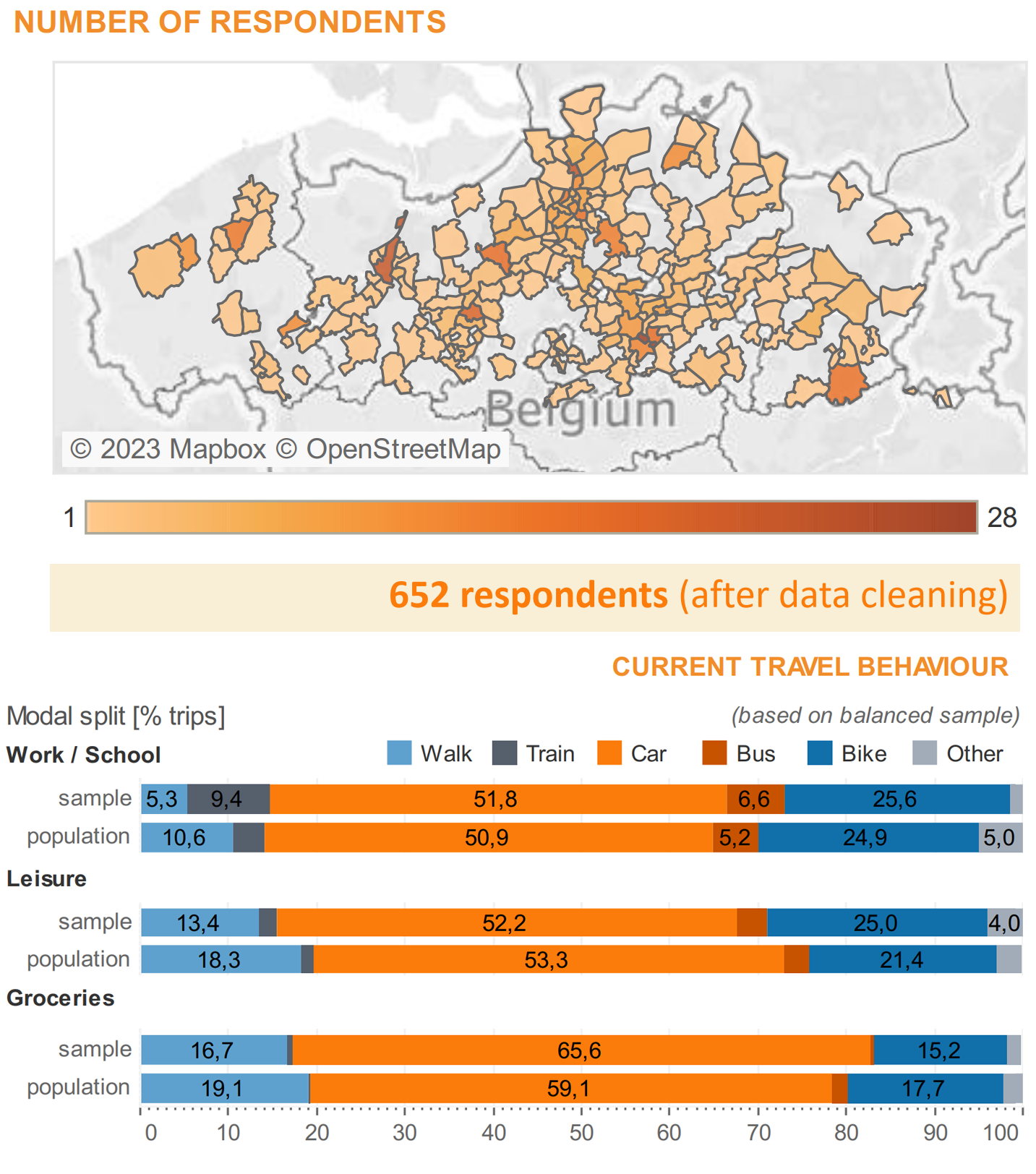
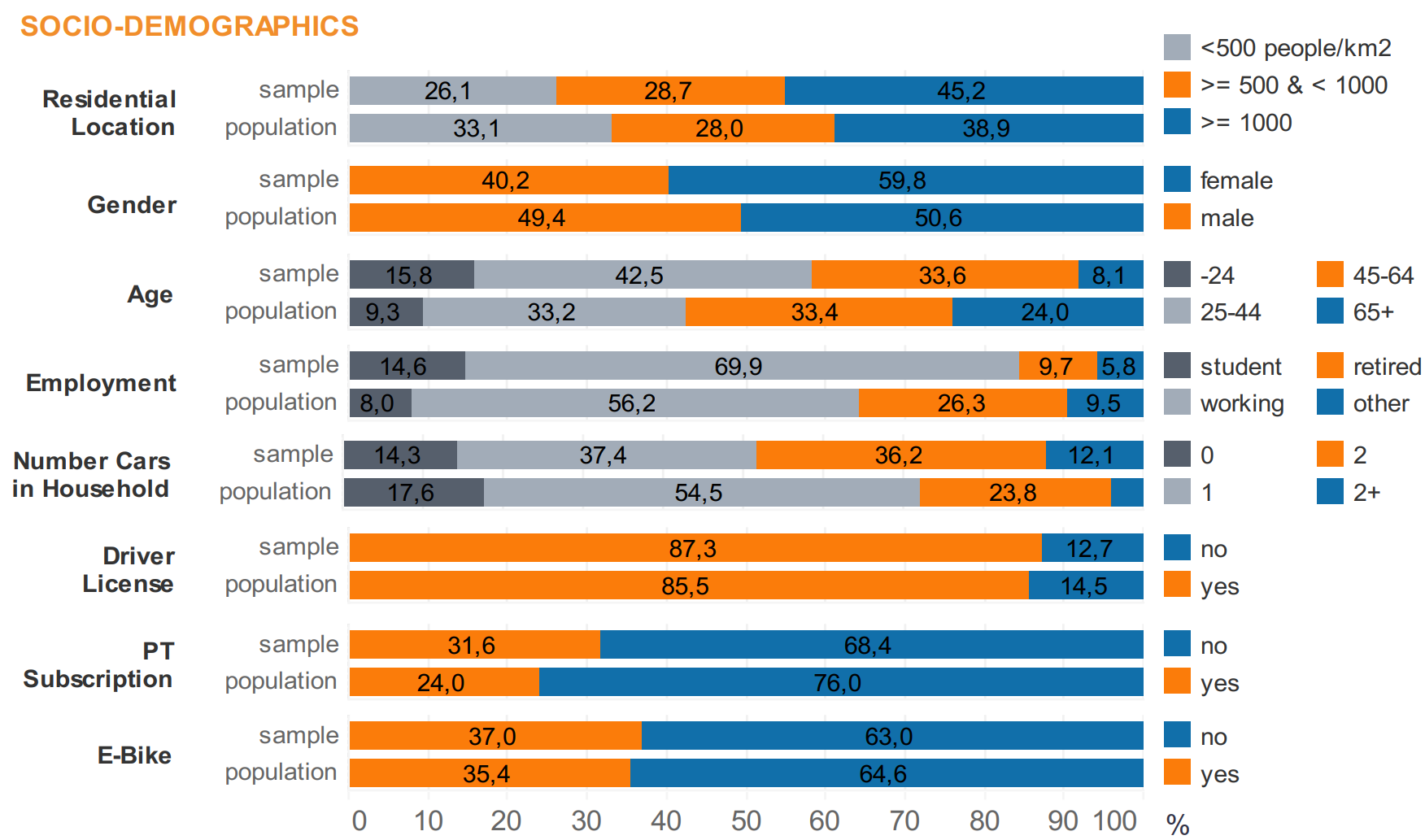
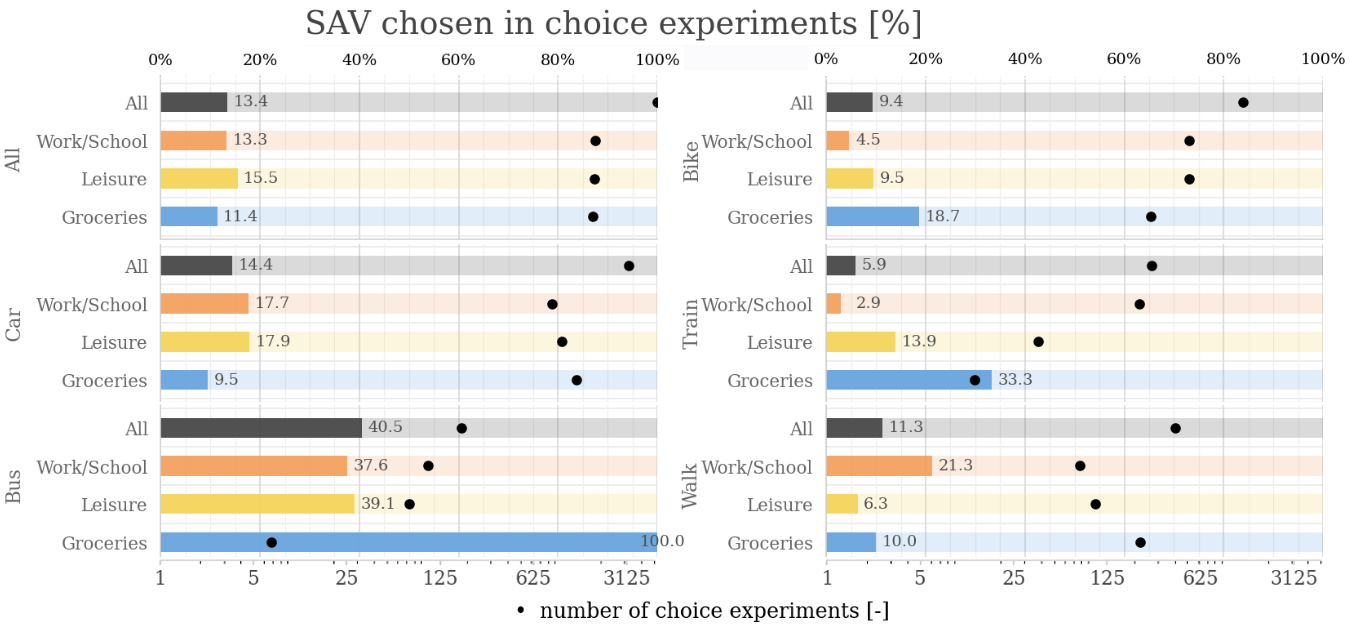
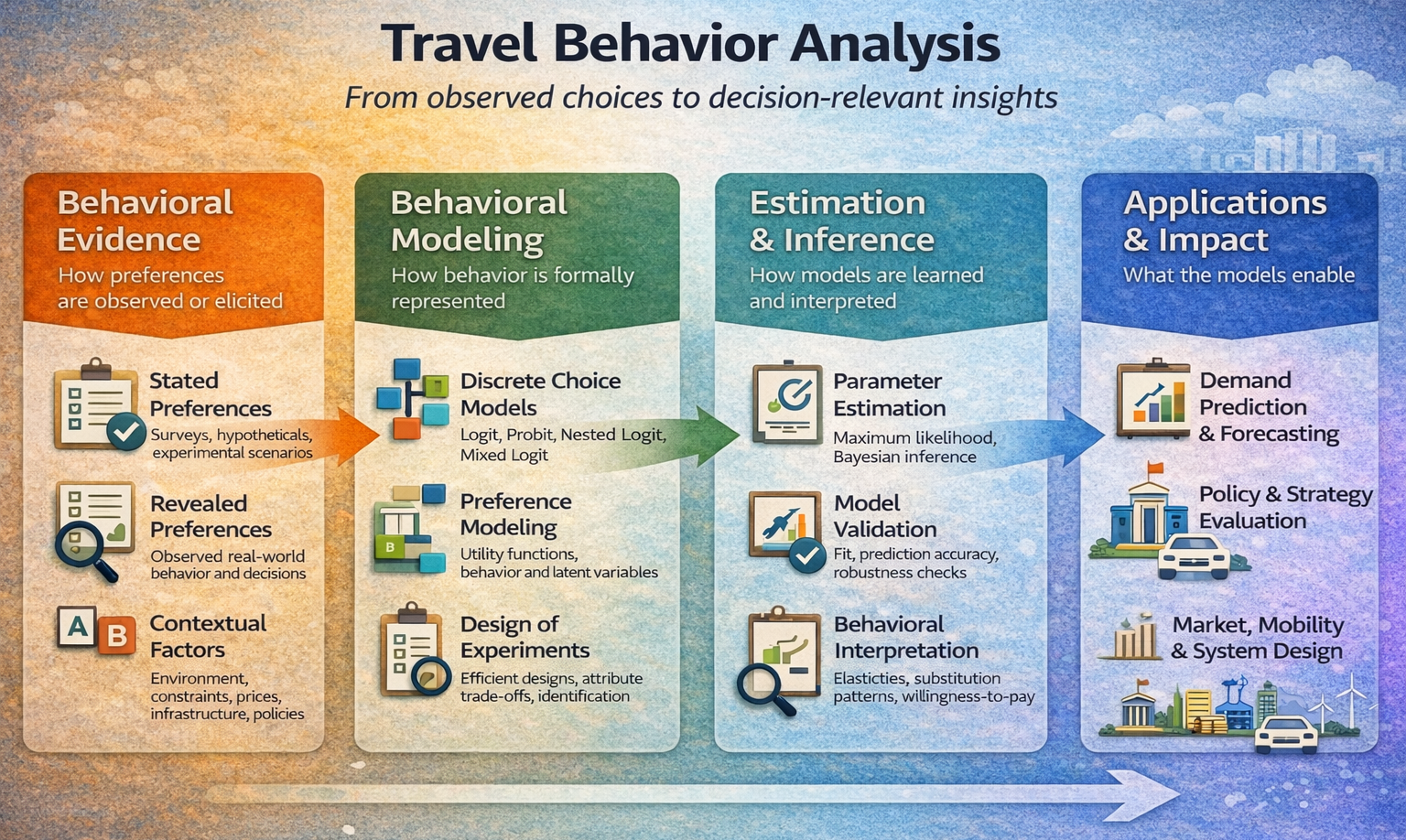
Travel behavior analysis applies this behavioral lens to how people organize activities and choose when, where, how, and whether to travel. Its primary purpose is to explain and forecast demand by explicitly modeling individual decision-making rather than relying solely on aggregate trends. Applications include travel demand forecasting, pricing and incentive design, mode choice and accessibility analysis, evaluation of new mobility services, and assessment of policy interventions related to sustainability and equity. By connecting socio-demographics, activity patterns, network conditions, and perceived costs, travel behavior analysis supports evidence-based planning and business decisions in contexts where demand is elastic, heterogeneous, and sensitive to both economic and non-economic factors.
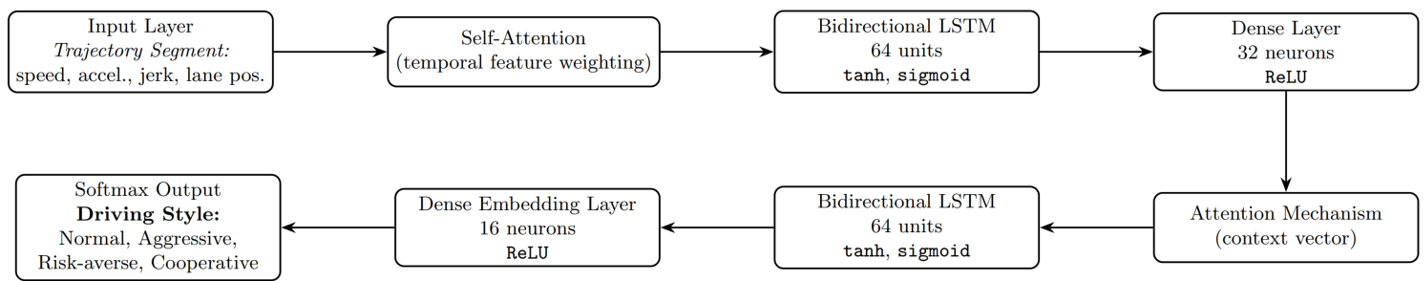
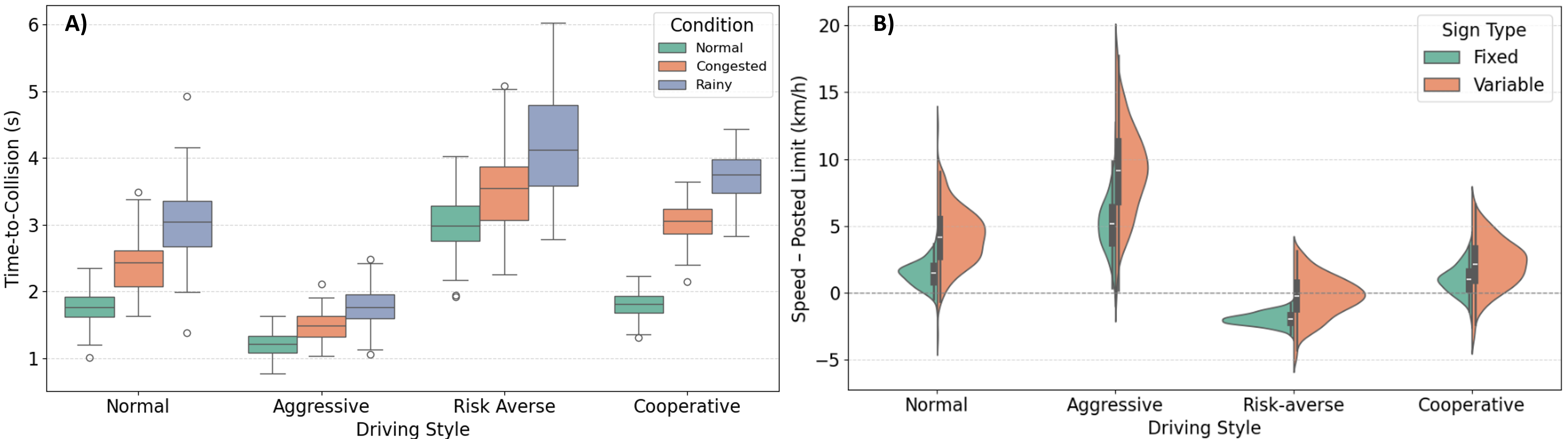
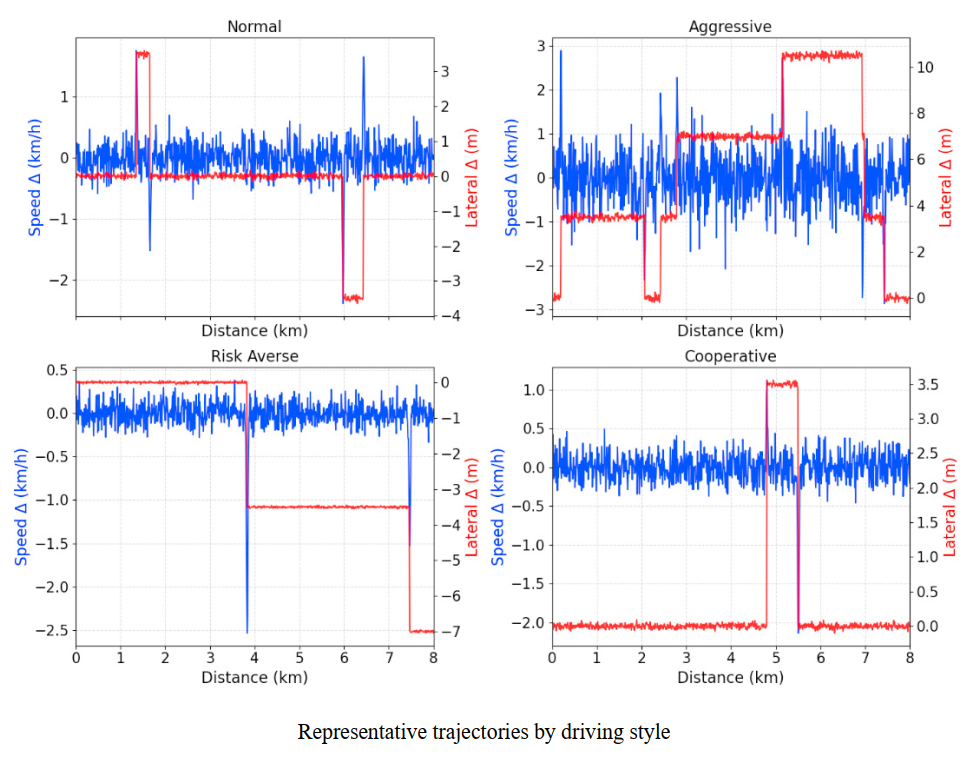
Driving behavior analysis shifts the focus from trip-level decisions to the tactical and operational choices made during driving, such as speed selection, car-following, gap acceptance, lane changing, and responses to traffic control or assistance systems. Its objectives include understanding heterogeneity in driving styles, identifying precursors to safety-critical events, and quantifying how drivers adapt to infrastructure, traffic conditions, and vehicle technologies. Practical applications span road safety assessment, risk modeling, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), connected and automated mobility, insurance analytics, and real-time traffic operations. From a data science perspective, driving behavior analysis bridges human factors with high-resolution sensor data, enabling interpretable models that inform both system design and real-time decision support.
The methodological foundation of behavioral analysis combines econometric modeling with experimental and data-centric approaches. Discrete choice analysis models decisions as outcomes of utility maximization, allowing preferences, trade-offs, and heterogeneity to be estimated in a statistically rigorous and interpretable manner. Design of experiments provides principled strategies to generate informative data by systematically varying attributes and conditions, improving identifiability and efficiency. Revealed preference methods infer behavior from observed real-world choices, capturing actual constraints and habits, while stated preference methods elicit responses to hypothetical scenarios to evaluate new policies, products, or technologies before deployment. Together, these methods form a coherent toolkit that is transferable across domains wherever understanding and predicting human decision-making is essential.
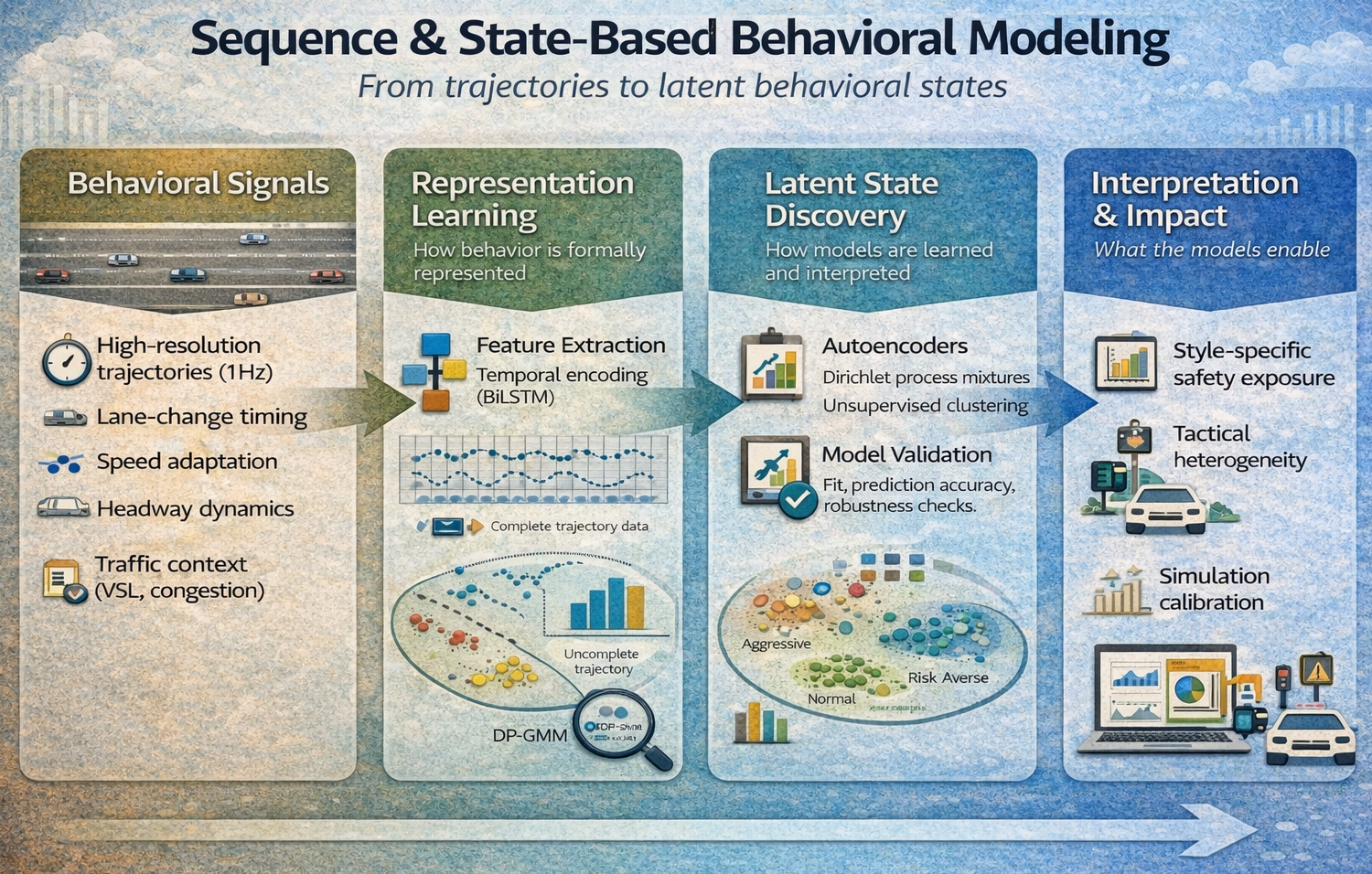
Across my projects, I have systematically applied the full spectrum of behavioral analysis methods: discrete choice analysis, rigorous data collection survey and companions for revealed preference analysis, and design of experiments for stated preference studies, covering the entire pipeline from hypothesis and assumptions definition to data collection to modeling, inference, and decision support. More recently, I have expanded this methodological foundation with unsupervised, neural-network-based classification and representation learning to uncover latent behavioral patterns and address behavioral heterogeneity at scale. This combination allows me to move seamlessly between interpretable, theory-driven models and data-driven discovery, enabling robust segmentation, explanatory insight, and predictive performance in complex, real-world settings where behavior is diverse, dynamic, and only partially observable.